|
The life Cycle of E.labbeana and E.columbarum. (The Causative Agent of Coccidiosis) |
||
|
|
||
|
|
← |
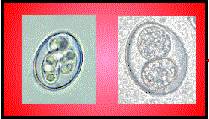
The oocysts complete development and become infective (sporulate) outside of the host’s body |
|
↓ |
|
↑ |
|
The infective oocyst are ingested by a host |
|
|
|
↓ |
|
| |
|
The oocyst “excysts” in the small intestine, and sporozoites infect the cells lining the small intestine |
|
Oocysts are passed in the feces of the infected host |
|
↓ |
|
↑ |
|
The parasite reproduces asexually in the cells of the small intestine producing merozoites. The merozoites infect more intestinal cells. |
→ |
After several generations of asexual reproduction, oocysts are produced |
|
↕ |
|
|
|
Asexual reproduction (schizongony or merogony) is self-limiting and ceases after several generations. Oocysts are produced only as long as schizogony continues. |
|
|